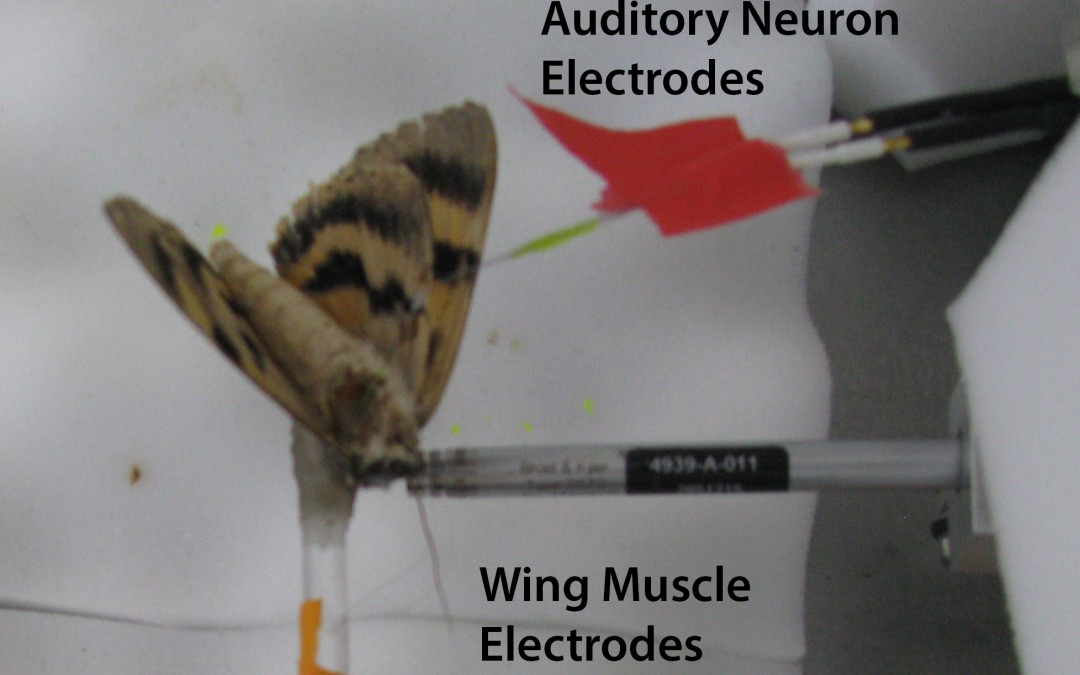
by Shira | Feb 2, 2018
Abstract: Animals co-occur with multiple predators, making sensory systems that can encode information about diverse predators advantageous. Moths in the families Noctuidae and Erebidae have ears with two auditory receptor cells (A1 and A2) used to detect the...
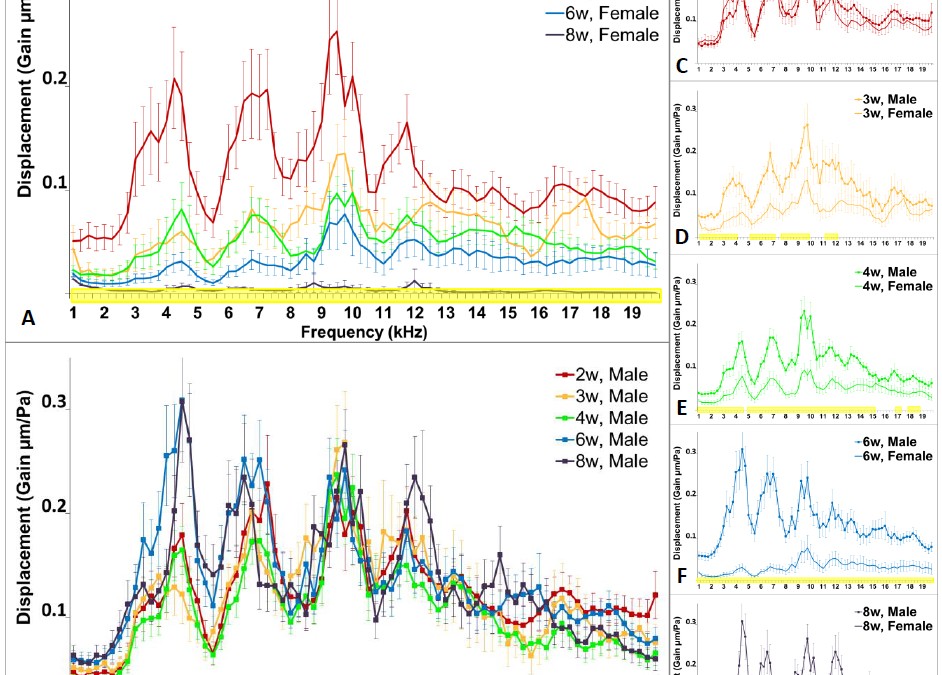
by Shira | Oct 9, 2016
Insects display signs of ageing, despite their short lifespan. However, the limited studies on senescence emphasize longevity or reproduction. We focused on the hearing ability of ageing adult locusts, Schistocerca gregaria. Our results indicate that the youngest...
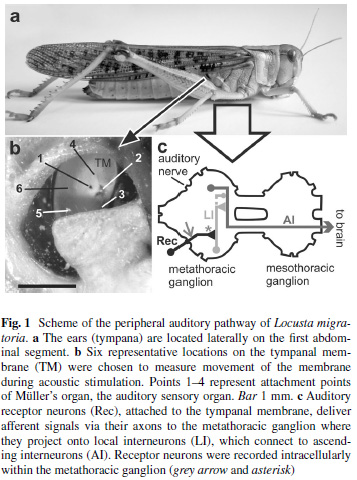
by Shira | Jun 29, 2014
Poikilothermic animals are affected by variations in environmental temperature, as the basic properties of nerve cells and muscles are altered. Nevertheless, insect sensory systems, such as the auditory system, need to function effectively over a wide range of...





Recent Comments