Publications
Please select a publication to view its abstract. Publications may be sorted by category.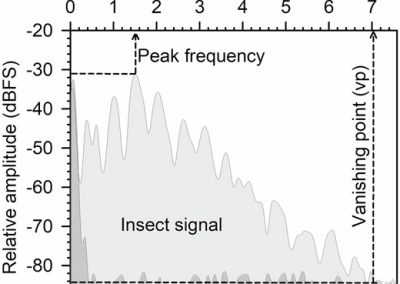
Krugner and Gordon. 2021. Mating Communication of the Variegated Leafhopper, Erasmoneura variabilis, With Notes on Vibrational Signaling of Other Grapevine Cicadellids in California
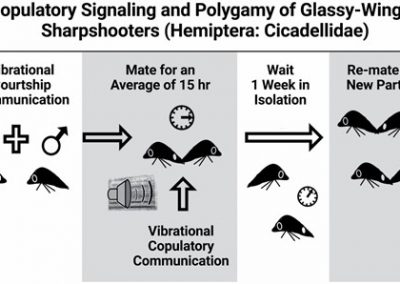
Gordon and Krugner 2021. Copulatory Signaling and Polygamy of Glassy-Winged Sharpshooters (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae)

Gordon and Krugner. 2019. Mating Disruption by Vibrational Signals: Applications for Management of the Glassy-Winged Sharpshooter. Book Chapter
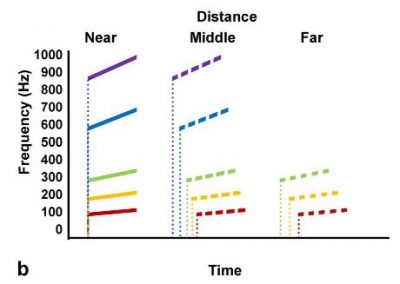
Gordon et al (2019) Transmission of the frequency components of the vibrational signal of the glassy‑winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca vitripennis,within and between grapevines
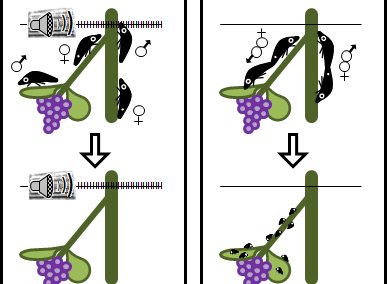
Krugner R, Gordon SD. 2018. Mating disruption of Homalodisca vitripennis (Germar) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) by playback of vibrational signals in vineyard trellis. Journal of Pest Management Science.
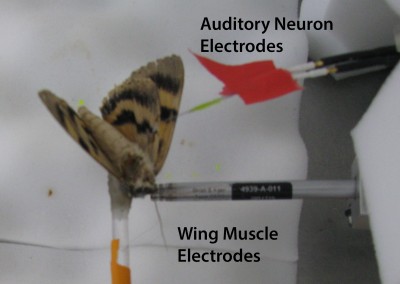
Gordon SD. ter Hofstede HM. 2018. The influence of bat echolocation call duration and timing on auditory encoding of predator distance in noctuoid moths. The Journal of Experimental Biology

Mazzoni V, Gordon SD, Nieri R, Krugner R. 2017. Design of a candidate vibrational signal for mating disruption against the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca vitripennis, Pest Management Science. 73:2328-2333.
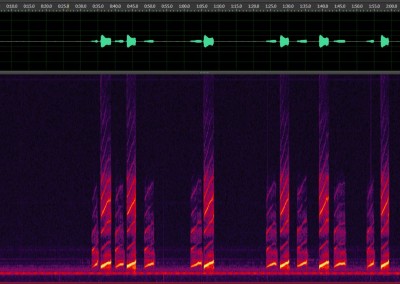
Gordon SD, Sandoval N, Mazzoni V, Krugner R. 2017. Mating interference of glassy-winged sharpshooters, Homalodisca vitripennis. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata. 164:27-34
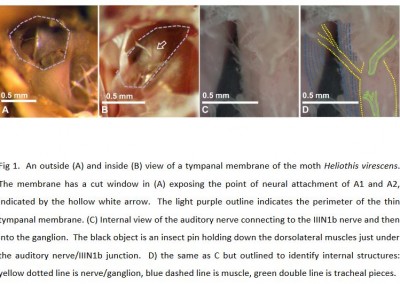
Gordon SD, Klenschi E, Windmill JFC. 2017. Hearing on the fly: the effects of wing position on noctuid moth hearing. Journal of Experimental Biology. 220:1952-1955

Nieri R, Mazzoni V, Gordon SD, Krugner R. 2017. Mating behavior and vibrational mimicry in the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca vitripennis. Journal of Pest Science. 90:887-889
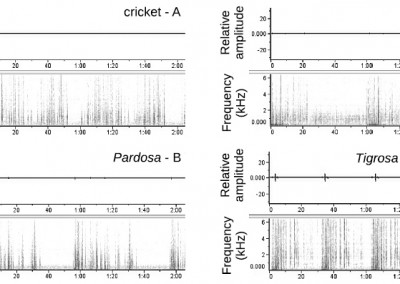
Sitvarin M, Gordon SD, Uetz GW, Rypstra A. 2016. The wolf spider Pardosa milvina detects predator threat level using only vibratory cues. Behaviour. 153:159-173
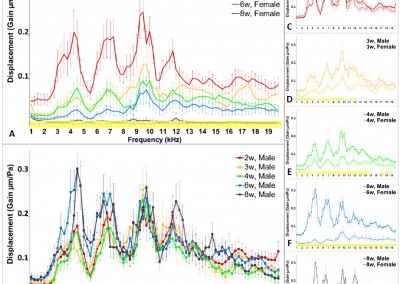
Gordon SD, Windmill JFC. 2015. Hearing ability decreases in ageing locusts. J. of Experimental Biology. 218:1990-199

Gordon SD, Jackson JC, Rogers SM, Windmill JFC. 2014. Listening to the Environment: Hearing Differences from an Epigenetic Effect in Solitarious and Gregarious Locusts. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 281 no. 1795 20141693
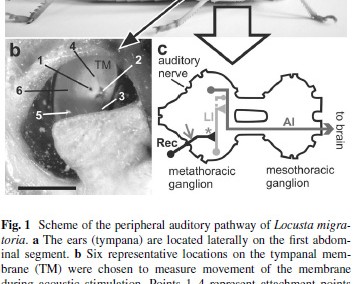
Eberhard MJB*, Gordon SD*, Windmill JFC, Ronacher B. 2014. Temperature effects on the tympanal membrane and auditory receptor neurons in the locust. Journal of Comparative Physiology A. 200:837-847 * These authors contributed equally

Mortimer B, Gordon SD, Holland C, Siviour CR, Vollrath F, Windmill JFC. 2014. The Speed of Sound in Silk: Linking Material Performance to Biological Function. Adv. Mater. 26:5179-5183.
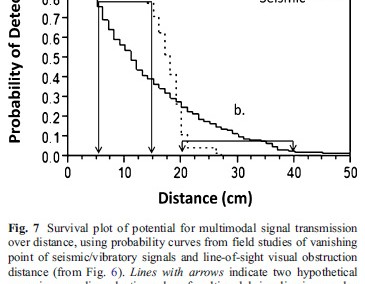
Uetz GW, Roberts JA, Clark DL, Gibson JS, Gordon SD. 2013. Active space of multimodal signals of wolf spiders in a complex litter environment. Behavioral Ecology & Sociobiology. 67:1471-1482
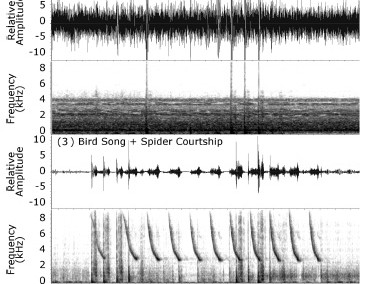
Gordon SD, Uetz GW. 2012. Environmental interference: impact of acoustic noise on seismic communication and mating success. Behavioral Ecology. 23:700-714.

Gordon SD, Uetz GW. 2011. Multimodal communication of wolf spiders on different substrates: evidence for behavioral flexibility. Animal Behaviour. 81:367-375.