by Shira | Mar 30, 2018
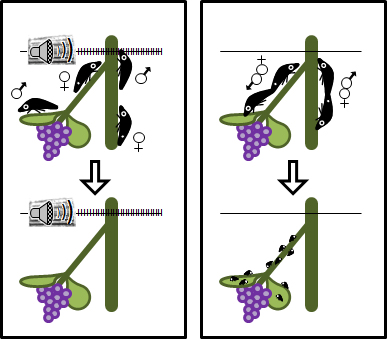
BACKGROUND Glassy-winged sharpshooter (GWSS), Homalodisca vitripennis (Germar) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) is an important vector of the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa, the causal agent of Pierce’s disease of grapevine. Area-wide insecticide applications have suppressed...
by Shira | Apr 11, 2017
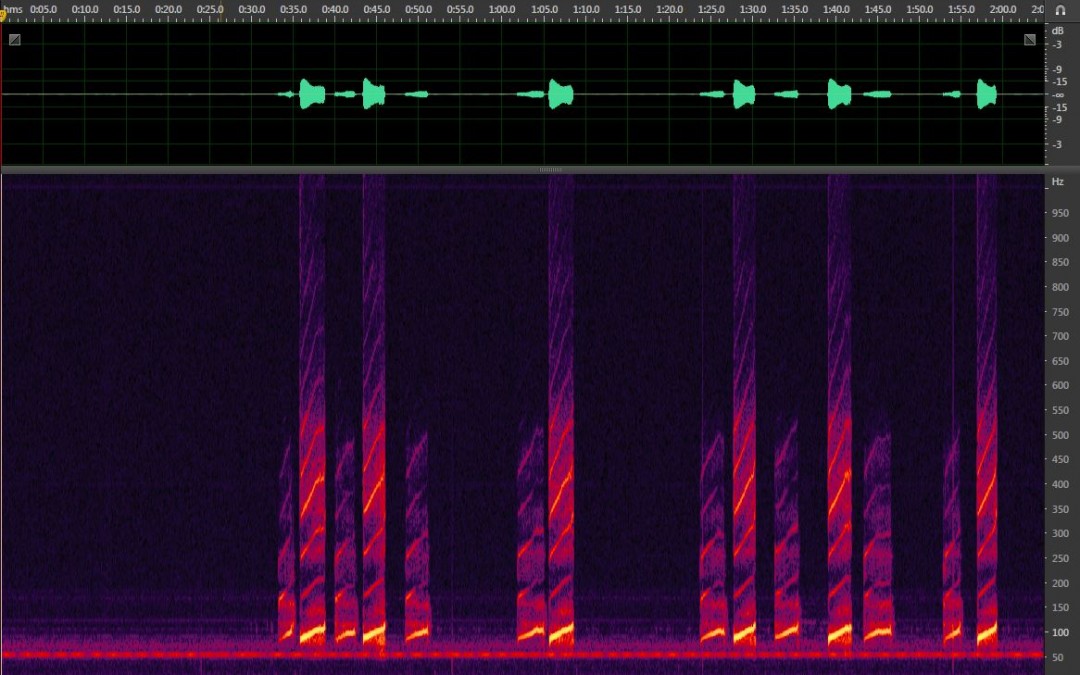
Animal communication is a complex behavior that is influenced by abiotic and biotic factors of the environment. Glassy-winged sharpshooters (GWSS), Homalodisca vitripennis (Germar) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae), primarily use vibrational signaling for courtship...





Recent Comments