
by Shira | May 19, 2017
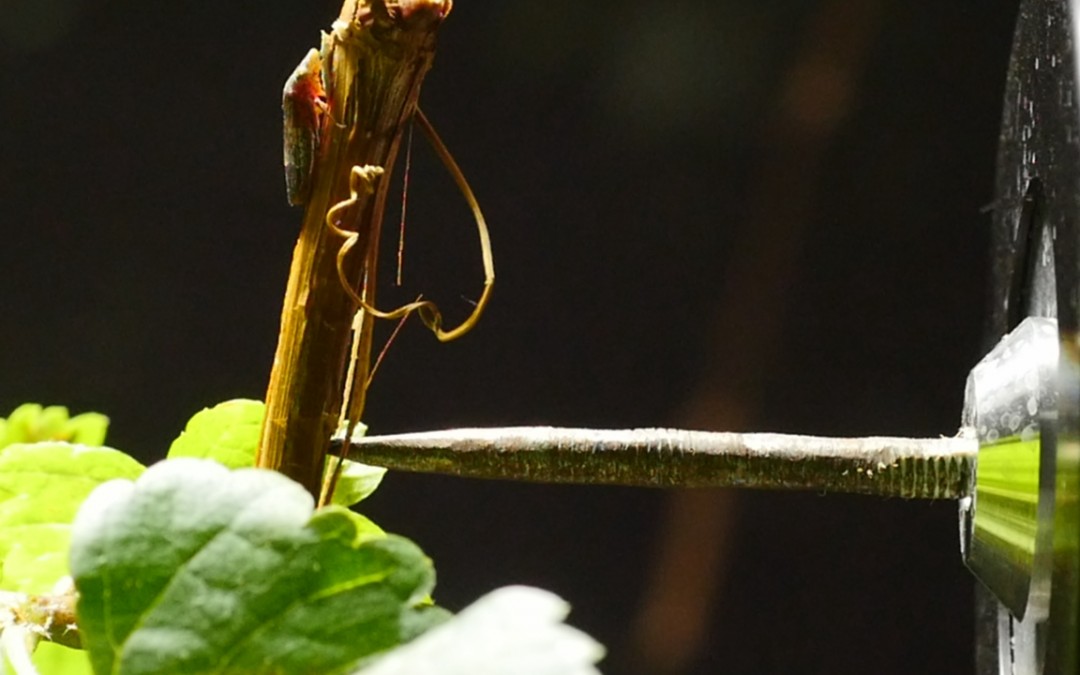
The glassy-winged sharpshooter (GWSS), Homalodisca vitripennis, is an important pest of grapevines due to its ability to transmit Xylella fastidiosa, the causal agent of Pierce’s disease. GWSS mating communication is based on vibrational signals; therefore,...
by Shira | Apr 11, 2017
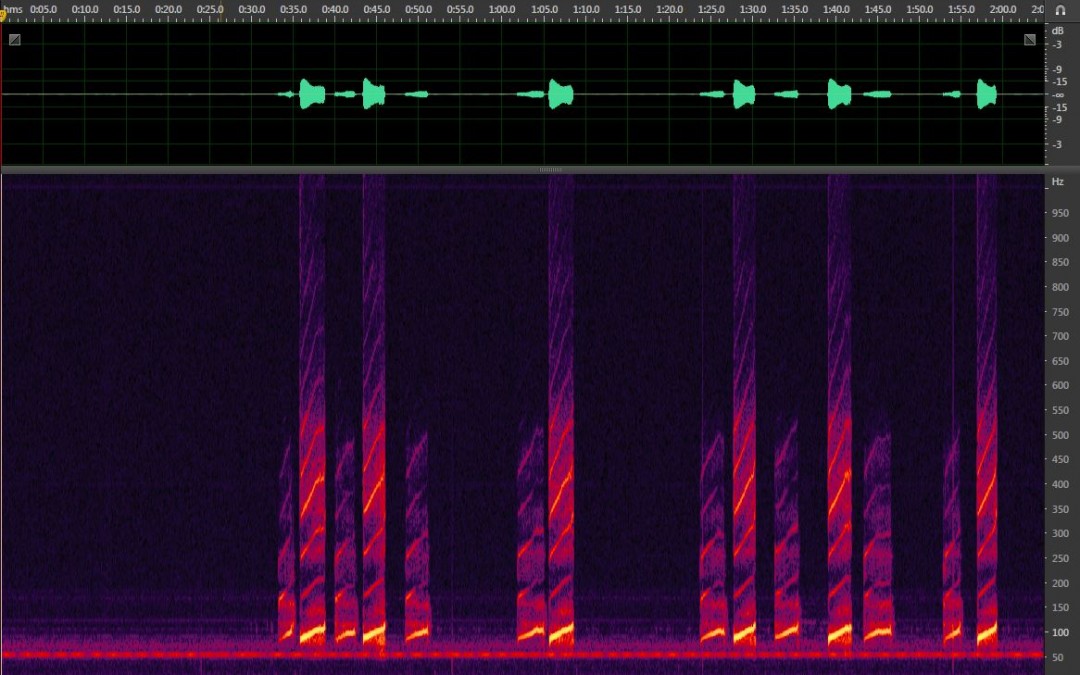
Animal communication is a complex behavior that is influenced by abiotic and biotic factors of the environment. Glassy-winged sharpshooters (GWSS), Homalodisca vitripennis (Germar) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae), primarily use vibrational signaling for courtship...
by Shira | Mar 21, 2017
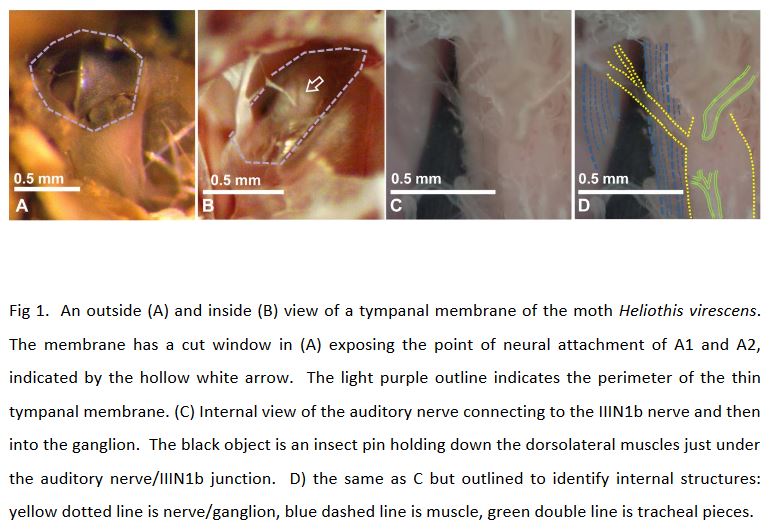
The ear of the noctuid moth has only two auditory neurons, A1 and A2, which function in detecting predatory bats. However, the noctuid’s ears are located on the thorax behind the wings. Therefore, since these moths need to hear during flight, it was hypothesized...

by Shira | Feb 18, 2017
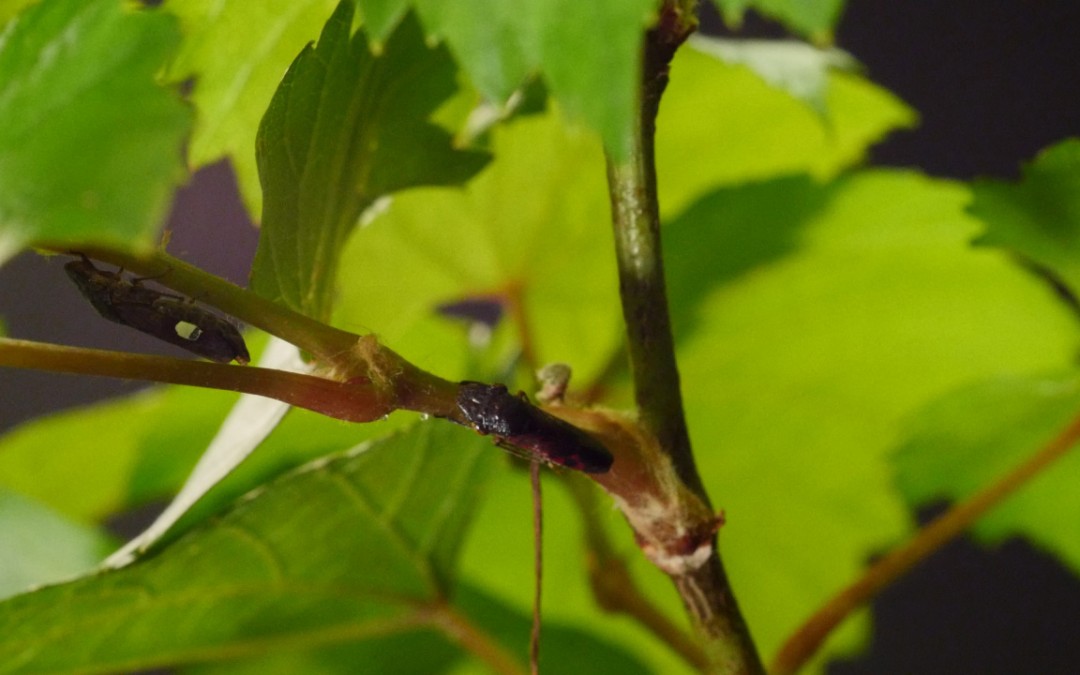
The glassy-winged sharpshooter (GWSS), Homalodisca vitripennis, is an important vector of Xylella fastidiosa, the causal agent of Pierce’s disease of grapevine. GWSS control relies mainly on insecticides; therefore, an alternative method, such as vibrational mating...
by Shira | Oct 9, 2016
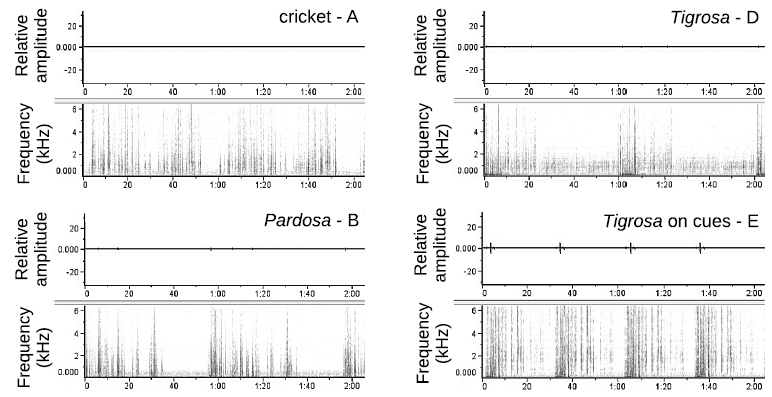
Predators may inadvertently signal their presence and threat level by way of signals in multiple modalities. We used a spider, Pardosa milvina, known to respond adaptively to chemotactile predator cues (i.e., silk, faeces and other excreta) to evaluate whether it...







Recent Comments